25 Data Analysis
25.1 Background
Data analysis skill is a necessity in current time independent of the domain. Even if you do not do it yourself, once you learn, it will help understand what are the possible options. It is a skill that can be applied in any professional or personal setup.
For all domains knowing basic data analysis using programming is essential.
For engineering and science domains the requirements are higher but the first step is the same.
Therefore, learning to do basic data analysis using programming is a common subset.
The data science section tries to give a simple overview of everything related to data, which should help identify the common subset and how it fits in the broader context of data science.
The objective is to provide an overview and then point to resources for learning more. Data analysis in itself requires a separate course in itself which fits in overall learning path related to programming and its applications.
25.1.1 Data Science
25.1.1.1 Terminology
Since the field of data is relatively new at this time and evolving very fast, the terminology is not consistent. The reasons for this rapid change are
- advancement in computing capacities
- advancement in storage capacities
- advancement in scope of data collection
Below are some key terms with an attempt to define them.
Data science is the field of study which is dedicated to studying data, scientifically. This includes all aspects of the data cycle which includes several subjects related to each stage in cycle, which may require applying knowledge of several other supporting subjects like math, computer science (software and hardware), domain specific knowledge, process and operations, etc.
Data Analytics is the skill to apply advanced math techniques, like statistics, machine learning and artificial intelligence, to model data to do predictive and prescriptive analysis using data.
Data analysis is the skill to do basic static analysis using data which answers questions related to past and present. This involves very basic math.
25.1.1.2 Data cycle
Data science is a new and very vast field with no consistent formalization of structure. The data cycle presented in this section will try to summarize and give an overview of different components of data science.
Any project related to data, irrespective of scale or domain, has some core elements.
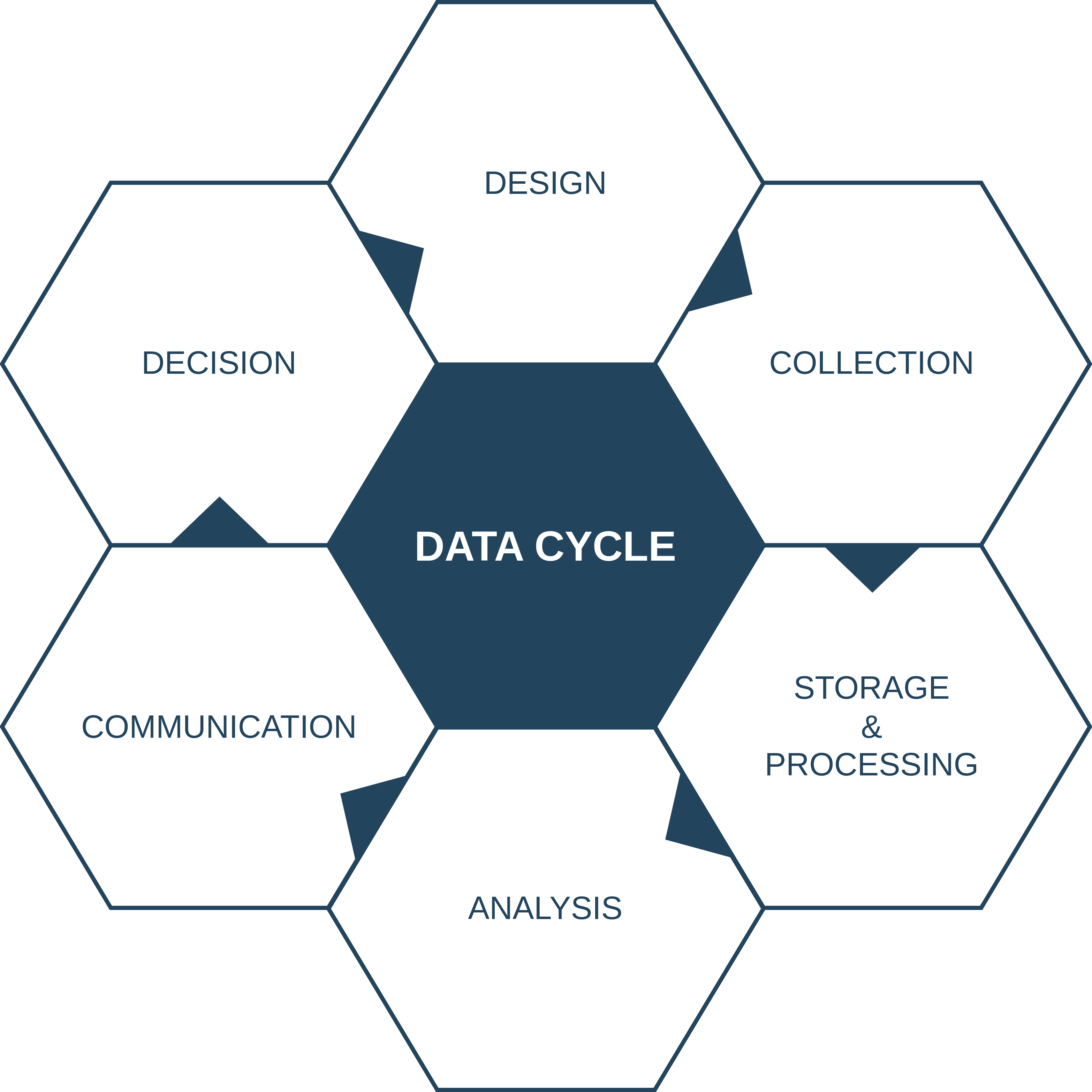
At small scale, one person might work on all elements. e.g. college projects requiring some analysis in which all stages can be performed using spreadsheets and programming.
At large scale, there might be multiple teams working on a single element. e.g. in a bank
- Design: All teams involved contribute to discussions
- Collection: All customers and several departments have access to corresponding applications which feed data to bank’s database servers
- Storage & Processing:
- There are multiple teams to perform validations and adjustments for loaded data coming in from different sources
- There are separate teams for managing database servers
- Analysis: There are multiple teams across multiple functions analyzing data
- Reporting: There are multiple reporting teams
- Decision: Business teams
25.1.1.2.1 Design
Design stage involves using knowledge of all the components, the target is to capture every aspect preemptively. For a large recurring project it might mean involvement of a large number of teams specialized in specific areas of the the data cycle.
Every data related project starts with designing decision stage, framing good questions that drive the project, but then it is an iterative process.
25.1.1.2.2 Collection
- Spreadsheets
- Web interface
- Desktop application
25.1.1.2.3 Storage & Processing
- Storage: excel, text files, database
- Processing
- Extract Transform Load (ETL) processes
- pre processing
- resolving duplicates
- bad data values
- missing data values
25.1.1.2.4 Analysis
- Levels of analysis
- Static: answers simple questions using historical data
- what has happened in the past?
- what is the current state?
- what is driving the current state?
- Predictive: answers more complex questions using math (probability and statistics)
- what would happen in future given a scenario?
- static models
- Prescriptive: answers more complex questions using math (probability and statistics)
- predict various scenarios
- answer, what should be done to ensure desired results?
- static models, more advanced than predictive models
- Machine learning, Artificial intelligence: come up with models based on data
- models train themselves based on data
- Static: answers simple questions using historical data
- Operational Process
- Extract
- Clean
- Analyze
- Model
- Visualization is part and key component of data analysis
25.1.1.2.5 Communication
- Components
- tables
- visualization
- theory: how you arrived at the results
- analysis: key findings
- recommendations
- Tools: documentation using programming
25.1.1.2.6 Decision
- Check if results are satisfactory, if not re-design in next cycle
- If there are new questions or findings, re-design in next cycle
25.1.2 Learning paths
25.1.2.1 Data analysis
Data analysis is generic and applicable to all domains. It requires to learn the basic usage of
- Data storage technologies: spreadsheets, comma separated files, databases
- Data analysis using programming
- import data in to a data structure on heap (RAM)
- operate on data
- visualization
- documentation of analysis and results
Steps involved in data analysis using programming
- Import data from excel, csv or txt files, database
- Clean data
- Analyze data by performing operations and visualization
- Document analysis and results
25.1.2.2 Data analytics
Data analytics is relevant for science and engineering fields. Data analysis is a pre-requisite for this. Additionally it requires learning more about below topics for coming up with models for prediction, prescription or machine learning and artificial intelligence.
- Math: statistics, machine learning, neural networks, etc.
- Advanced knowledge of technologies used, including programming
25.2 Data analysis in Python
Data analysis in python is mostly supported through pandas, which is one of the most popular packages on PyPI for data science.
Below are some resources to get started with data analysis using python.
Note that the resources are meant for the STEM audience so not everything will be in scope for generic audience. Still some initial chapters that focus on basic data analysis should be useful.