1 Background
1.1 Definition
Computer hardware is a machine which can be configured to do several tasks as needed.
A program, in context of computers, is a set of instructions for the computer. A program is also referred to as software.
Configuring the computer hardware to do some tasks to solve a problem is called programming.
1.2 Hardware
There are a lot of good short videos on web which you get by searching, e.g. “how do computers work”. It is worth spending some hours on this general search given the amount of time spent with technology.
Understanding everything in detail is beyond the scope. Still it is helpful to understand the flow of information and operations at a high level.
Computers are based on binary arithmetic. Computer hardware comprises of a large number of electronic circuits which communicate with each other through electrical signals, which essentially means communicating in binary, 0 or 1. The hardware is designed to understand different sequences of binary signals to perform different tasks.
Data and instructions are stored in binary format. 1 bit is the atomic unit of storage which stores 0 or 1. Instructions are also data in terms of computer memory, but usually term “data” is used for static information other than instructions.
At most basic level, hardware operates using below basic elements
- CPU: central processing unit or processor
- ALU (Arithmetic logic unit): operates on very small amount of binary data to perform arithmetic and logical operations
- Controller unit: controls the input/output signals from/to different parts of the computer
- Registers: smallest memory, closest to processing
- Cache (L1, L2, L3): next level memory for preprocessing
- RAM: random access memory
- larger than CPU cache but smaller than hard disk
- slower than CPU cache but faster than hard disk
- all data slots are equally accessible in same time
- Hard drive: long term storage
- largest in size but slowest
- Input/output devices: keyboard, mouse, monitor, speakers
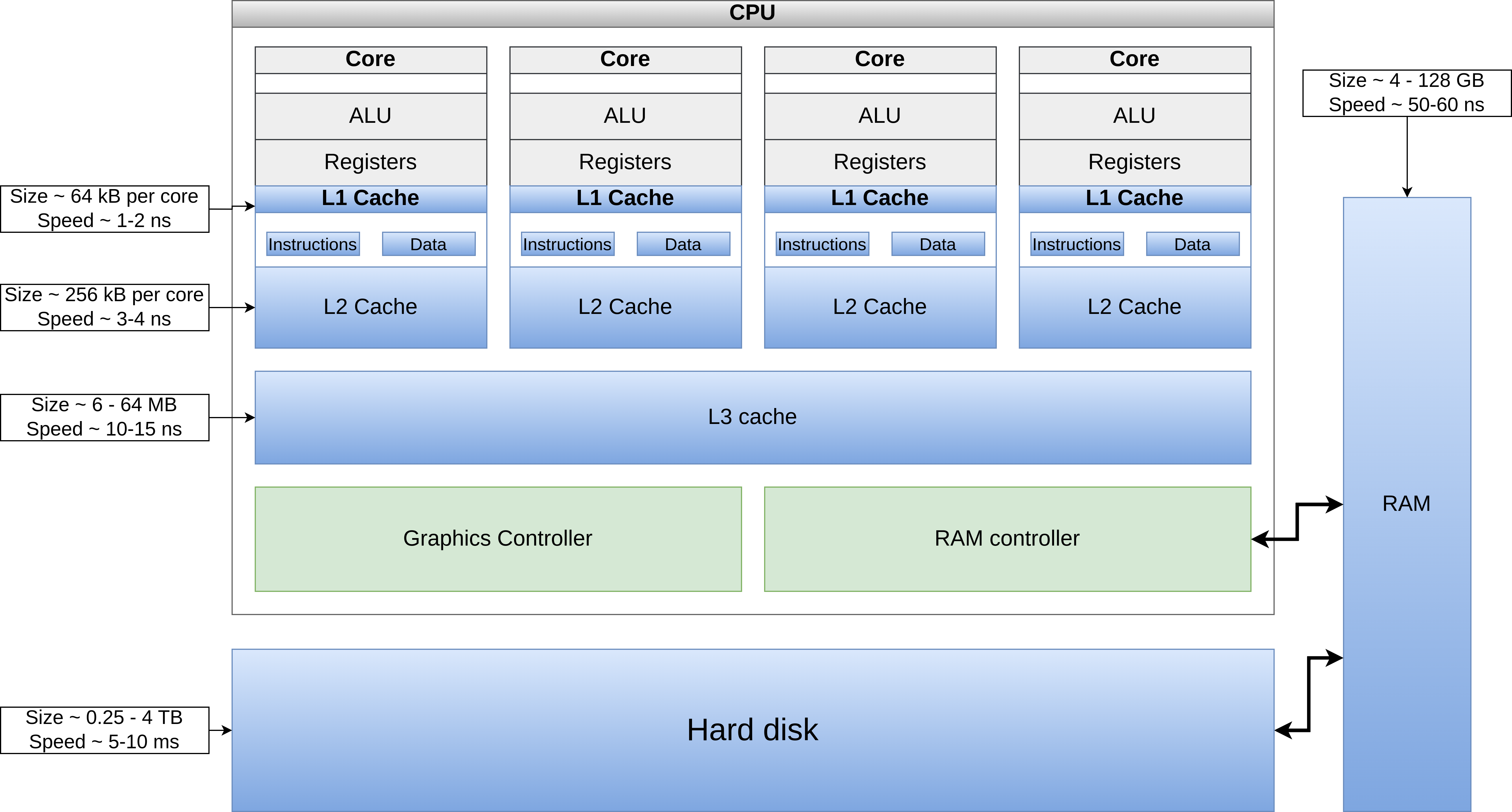
The CPU decides the architecture of information flow in a computer. Architecture has 2 main components related to design of conversion to machine code
- Instruction set architecture (ISA) that processor follows, e.g. x86-64, ARMv8-64
- Processing Width: maximum number of bits the processor can process at a time
- currently most CPU’s support 64 bit, earlier it was 32 bit
- the 64 in x86-64, ARMv8-64 is 64 bit width
1.3 Programming hardware
The computer hardware understands machine code, which is in binary, but it is not feasible to write, read and modify the machine code.
For illustration, if 010011001010 ... is a set of instruction in binary to tell the computer to beep, in programming language you type beep, the code will be mapped to instruction in binary and sent to processor.
Therefore programming language is needed. The key idea is to have a set of instructions in natural language which can be mapped to different set of instructions in machine code.